Why are eggs different colours?
Depending on the breed of chicken, most eggs are uniform in colour, ranging from white, pink and green, through to dark brown and blue.
Farming insects
The UN’s Food and Agricultural Organisation suggests that if we could farm insects on a commercial scale, food insecurity in many developing nations would be a thing of the past.
Career focus: Animal health Technician
As an animal health technician, your chief task will be to help look after farm animals, says Prof Cheryl McCrindle of the University of Pretoria.
Piggery ventilation
Ventilation control is one of the most important aspects in the planning and design of a piggery.
10 ways to make sure your poultry stay healthy
Backyard chickens can be a highly successful source of eggs and meat – as long as you look after them, says Prof Cheryl McCrindle.
A career in veterinary nursing
Veterinary nurses assist veterinarians in caring for animals. Prof Cheryl McCrindle discusses how to enter this profession.
Boost your biosecurity
Precautions should be taken to protect a herd against diseases acquired through outside contact.
African and Asiatic redwater in cattle
Redwater is an important tick-borne disease in cattle. In South Africa it accounts for losses of millions of rands annually. Dr JH du Preez and Dr Faffa Malan discuss the disease’s distribution, transmission, treatment and efficient management and control through blood vaccine.
Dealing with the ‘silent disease’ – measles
Cases of measles are frequently found in slaughter stock.
Managing trichomoniasis
Beef management consultant Barry Symons tells Lloyd Phillips how to go about dealing with this serious disease.
Intensive vs extensive farming
In the trend towards increasingly extensive livestock production, are we not moving too far from natural production systems and placing our hope in feed from a bag? Roelof Bezuidenhout poses the question.
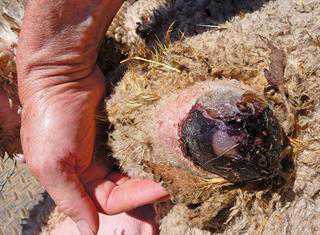
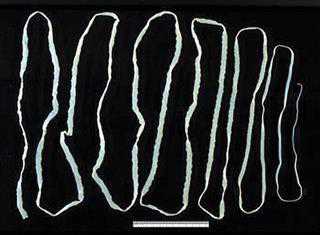
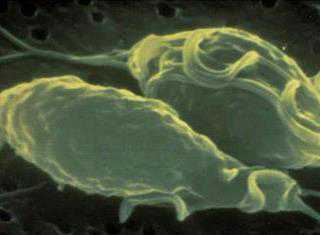
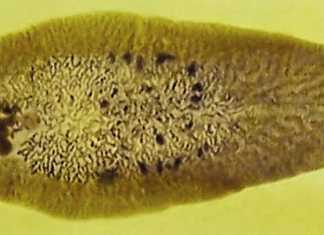
Controlling liver fluke disease
Fasciolosis is a disease found worldwide. According to reports, its incidence is increasing in certain regions.
Keeping records for layers
A management calendar is crucial for success even if you are simply supplying eggs to your own family.
Farming eggs for family and profit
How to build, manage and maintain your own affordable household egg production unit.
Preventing zoonosis
Controlling the spread of diseases to humans is generally easy, as most of the measures are grounded in common sense, writes Paul Donovan.
Feeding pen problems
Rounding off lambs under intensive conditions requires sound management, especially of aspects such as disease prevention and housing.
- ADVERTISEMENT -
- ADVERTISEMENT -
MUST READS
- ADVERTISEMENT -