Farming eggs for family and profit
How to build, manage and maintain your own affordable household egg production unit.
Preventing zoonosis
Controlling the spread of diseases to humans is generally easy, as most of the measures are grounded in common sense, writes Paul Donovan.
Feeding pen problems
Rounding off lambs under intensive conditions requires sound management, especially of aspects such as disease prevention and housing.
Rounding off lambs in a feeding pen
When mutton prices are high or grazing is scarce, this practice can be extremely profitable.
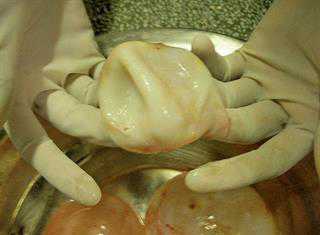
Dealing with hydatid disease
This parasitic disease, caused by the tapeworm E. granulosus, affects cattle, sheep, goats and even humans.
Home-made tonic for sheep
Roelof Bezuidenhout recommends this remedy to boost your sheep’s condition.
Ticks: a major parasite
It is estimated that tick-borne diseases kill more than a million cattle a year in Africa. This amounts to a loss of more than R1,6 billion.
Lactation begins at dry-off!
During its dry period, a cow is heavily pregnant with a fast-growing foetus. This is a very important time in her production cycle, and nutrition must not be neglected.
How to identify different ticks
Ticks are the most common external parasite of livestock and are vectors for a number of serious diseases. We list and describe some of the more common ticks.
Ticks – a dangerous pest
Ticks are the most common external parasite of livestock and are vectors for a number of serious diseases, cautions Paul Donovan.
Redwater (Tick-borne disease)
Redwater is a disease affecting cattle and is transmitted by infected blue ticks occuring in the higher rainfall regions of South Africa, such as the Western and Eastern Cape, KwaZulu-Natal...
Bluetongue (Midge-borne disease)
“Bluetongue is transmitted by the Culicoides midge, which breeds in moist, warm conditions,” says Dr Leask.